why ketoacidosis in type 2 diabetes Diabetes and fruity breath: causes, risks, and treatment
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that can be life-threatening if not promptly diagnosed and treated. It occurs when the body is unable to use glucose for fuel due to a lack of insulin and starts breaking down fats instead. This process leads to the production of ketones, which, when accumulated in the blood, can cause a series of metabolic abnormalities. To better understand the pathophysiology of DKA, let’s take a closer look at the steps involved in its development. The first stage is insulin deficiency, which can be caused by various factors such as missed doses of insulin, illness, or certain medications. Without enough insulin, glucose cannot enter the cells, leading to a buildup of sugar in the blood. As the body senses the lack of energy, it begins to break down fat stores into fatty acids. These fatty acids are then converted into ketones by the liver through a process called ketogenesis. In normal circumstances, ketones are used as an alternative fuel source during periods of fasting or prolonged exercise. However, in DKA, ketone production exceeds the body’s ability to utilize them. The accumulation of ketones in the blood leads to a state of metabolic acidosis. The acidic environment disrupts normal cellular function and can affect various organs. One of the early signs of metabolic acidosis is deep, rapid breathing, known as Kussmaul breathing. This type of breathing is the body’s attempt to eliminate excess carbon dioxide and compensate for the acidosis. As DKA progresses, electrolyte imbalances can occur. The loss of fluids through excessive urination, along with vomiting and dehydration, can lead to decreased levels of potassium, sodium, and chloride in the blood. These imbalances can further disrupt normal cellular function and lead to complications such as cardiac arrhythmias. Early recognition and treatment of DKA are essential to prevent severe complications. If you have diabetes and experience symptoms such as frequent urination, excessive thirst, fatigue, and fruity breath odor, it is crucial to seek medical attention promptly. A thorough evaluation, including blood tests and urine analysis, can confirm the diagnosis of DKA. The treatment of DKA involves a multidimensional approach. Intravenous fluids are administered to correct dehydration and restore electrolyte balance. Insulin therapy is initiated to lower blood sugar levels and promote the entry of glucose into cells. Potassium supplementation may also be necessary to maintain proper levels in the body. In conclusion, understanding the pathophysiology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) is crucial in the early recognition and management of this serious complication of diabetes. Recognizing the subtle signs and symptoms can help individuals seek timely medical attention and prevent life-threatening consequences. Remember, if you have diabetes and experience any concerning symptoms, always consult with your healthcare provider for proper evaluation and treatment. Sources: - “Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) Algorithm - Manual of Medicine” - “Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) – Why should it matter to me? | Nipro”
If you are searching about Diabetes and Fruity Breath: Causes, Risks, And Treatment you’ve came to the right place. We have 5 Pictures about Diabetes and Fruity Breath: Causes, Risks, And Treatment like Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) – Why should it matter to me? | Nipro, Diabetes and Fruity Breath: Causes, Risks, And Treatment and also Diabetes and Fruity Breath: Causes, Risks, And Treatment. Read more:
Diabetes And Fruity Breath: Causes, Risks, And Treatment
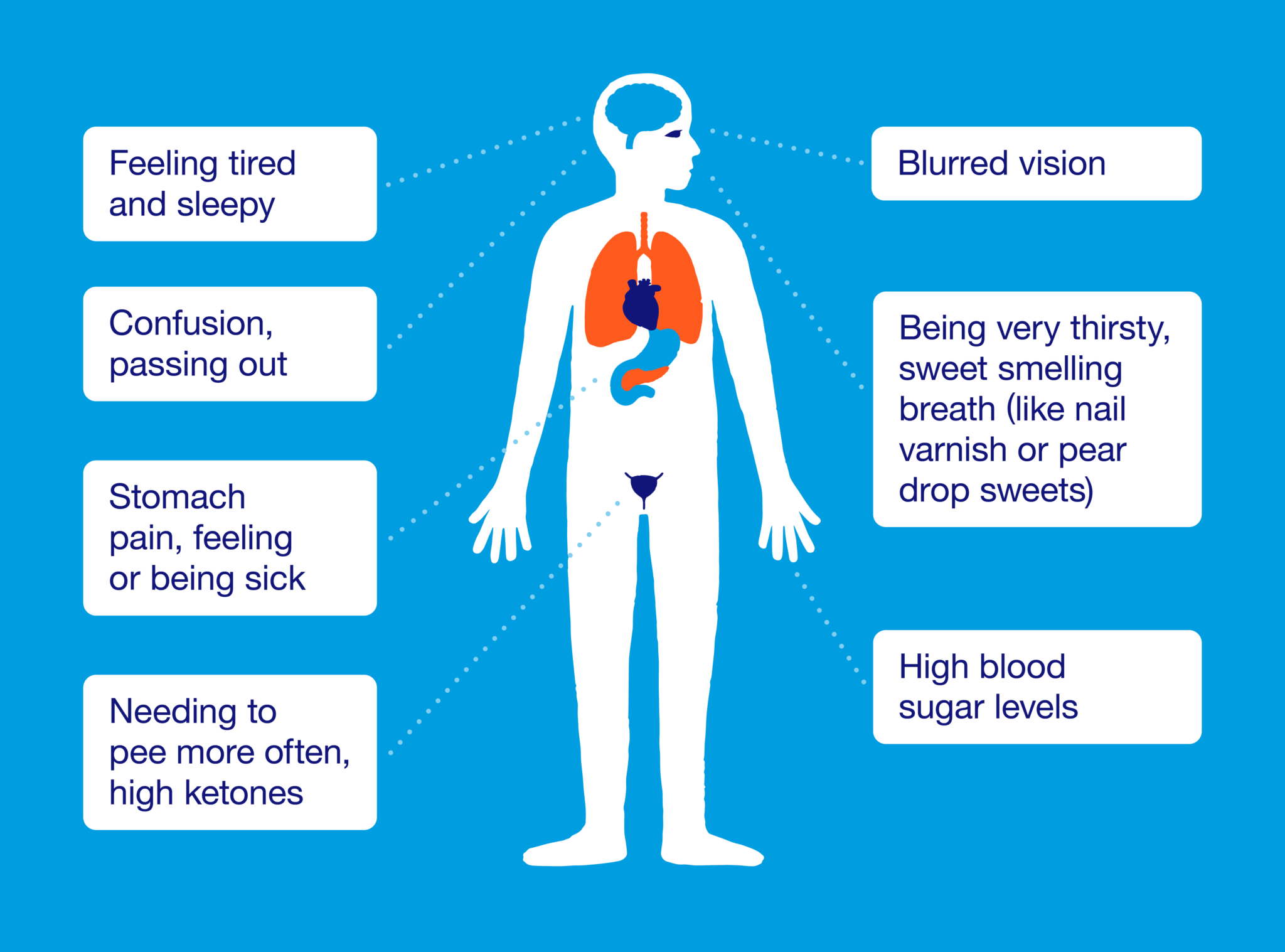 mantracare.orgketoacidosis diabetic dka breath treatment complications fruity ketosis symptome mellitus ketones urine mantracare anzeichen abdominal ursachen nausea difficulty remedies
mantracare.orgketoacidosis diabetic dka breath treatment complications fruity ketosis symptome mellitus ketones urine mantracare anzeichen abdominal ursachen nausea difficulty remedies
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) – Why Should It Matter To Me? | Nipro
 www.nipro-group.comketoacidosis dka diabetes nipro matter knowledge studying icu
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) Algorithm - Manual Of Medicine
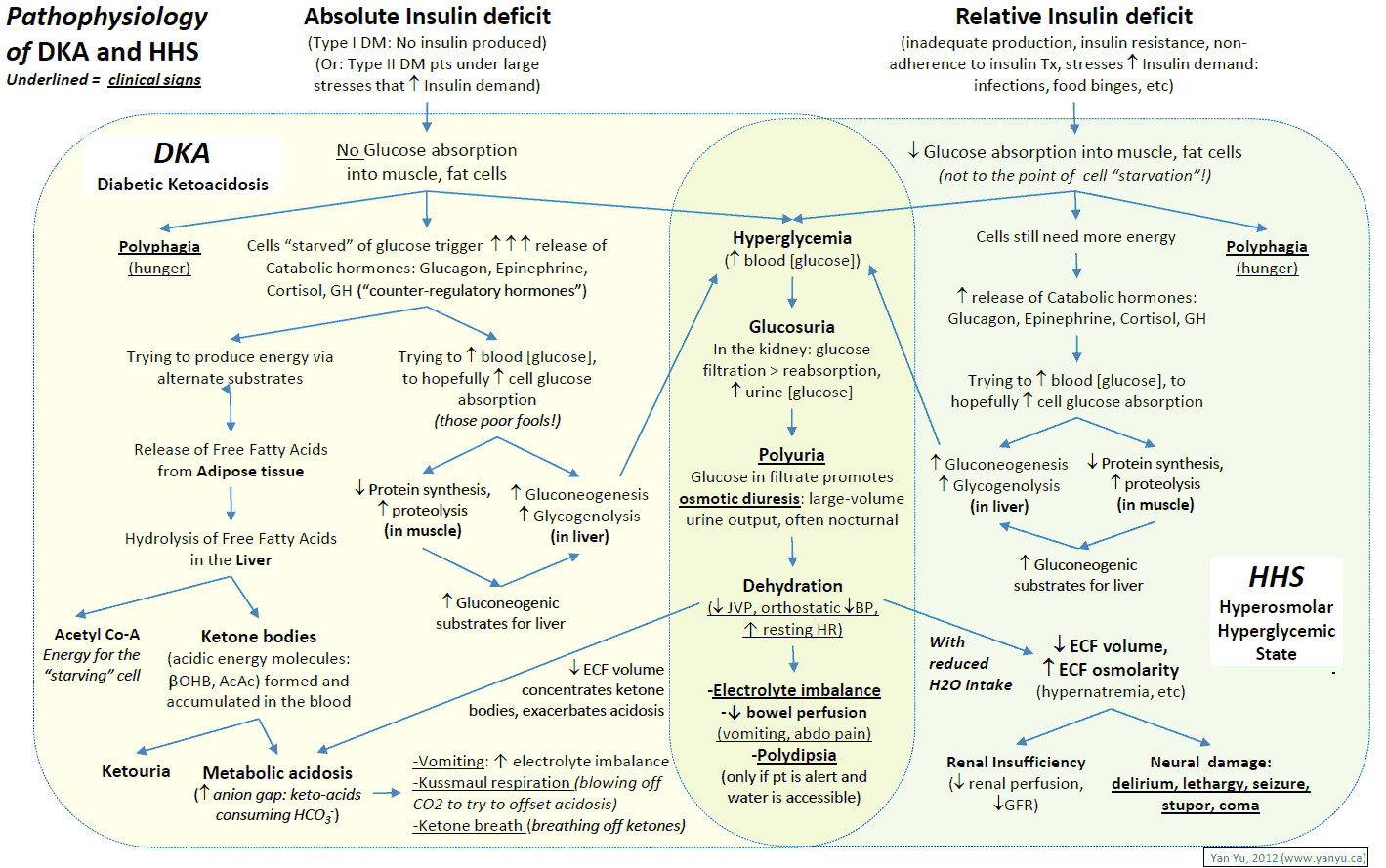 manualofmedicine.comketoacidosis dka diabetic pathophysiology algorithm kussmaul acidosis grepmed hhs hyperosmolar hyperglycemic respiration dehydration hypotension acetone labored breathing tachycardia
manualofmedicine.comketoacidosis dka diabetic pathophysiology algorithm kussmaul acidosis grepmed hhs hyperosmolar hyperglycemic respiration dehydration hypotension acetone labored breathing tachycardia
SGLT2 Inhibitor-induced Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Renal Fellow
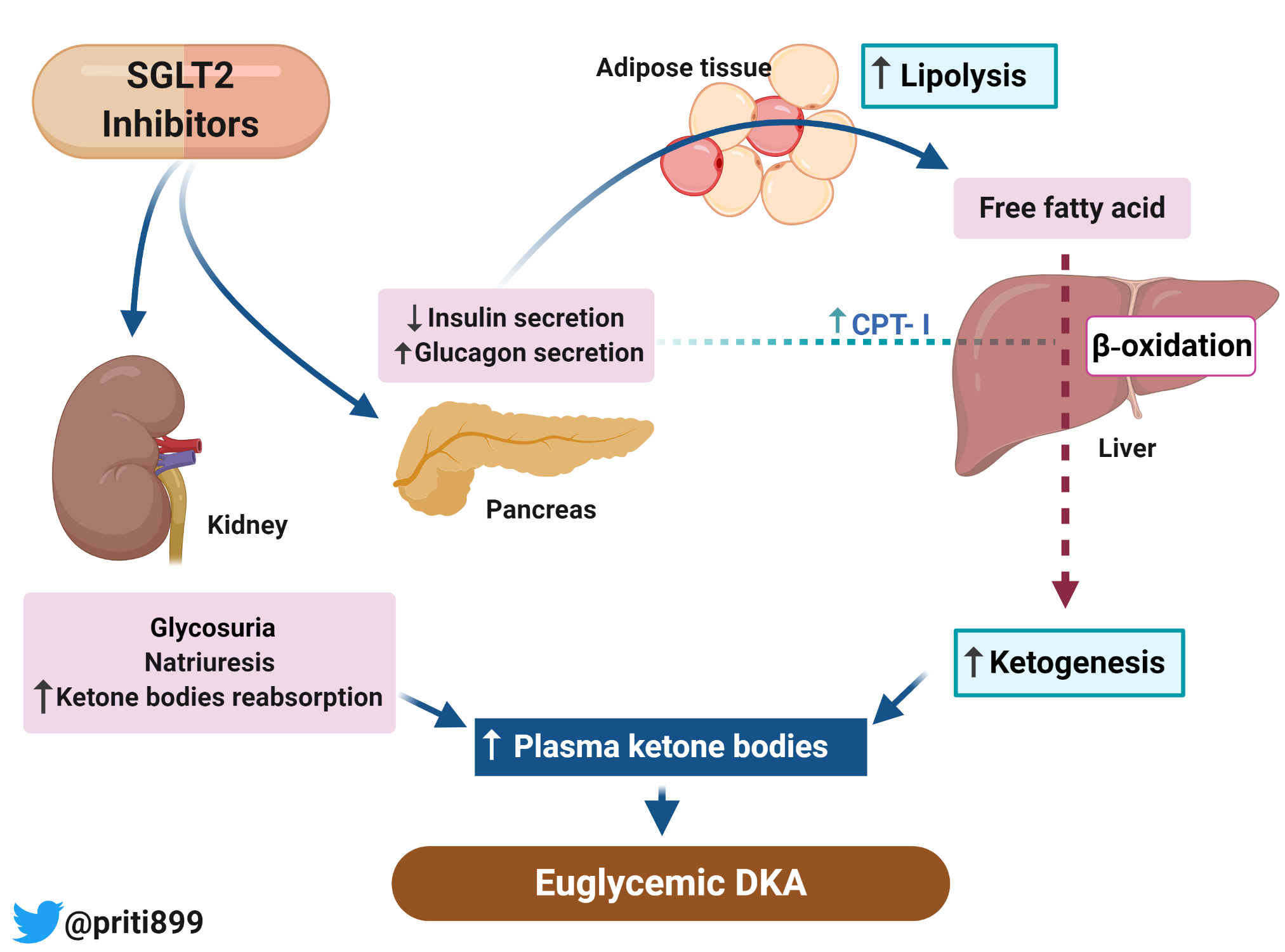 www.renalfellow.orgketoacidosis sglt2 euglycemic inhibitor induced urine sediment mitochondria transplantation principles immunologic bacterial forms renal renalfellow
www.renalfellow.orgketoacidosis sglt2 euglycemic inhibitor induced urine sediment mitochondria transplantation principles immunologic bacterial forms renal renalfellow
Aldosterone In Dka | DiabetesTalk.Net
 diabetestalk.netketoacidosis diabetic diabetes type ketosis pediatric dka starvation population insulin figure symptoms signs aldosterone diabetestalk quizlet sign
diabetestalk.netketoacidosis diabetic diabetes type ketosis pediatric dka starvation population insulin figure symptoms signs aldosterone diabetestalk quizlet sign
Sglt2 inhibitor-induced euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis. Diabetic ketoacidosis (dka) algorithm. Ketoacidosis diabetic dka breath treatment complications fruity ketosis symptome mellitus ketones urine mantracare anzeichen abdominal ursachen nausea difficulty remedies