are ketones acidic or basic Ketones and nutritional ketosis: basic terms and concepts
In today’s post, we are going to explore the fascinating world of ketones and glucose. These two compounds play crucial roles in our bodies and have distinct characteristics that set them apart. Let’s dive in and uncover the key differences between ketones and glucose!
Ketones
 Ketones, also known as ketone bodies, are organic compounds that our bodies produce during certain metabolic processes. They are derived from fatty acids and are primarily utilized as an alternative source of energy when glucose levels are limited.
Ketones, also known as ketone bodies, are organic compounds that our bodies produce during certain metabolic processes. They are derived from fatty acids and are primarily utilized as an alternative source of energy when glucose levels are limited.
One of the major roles of ketones is in providing fuel for our brain, especially during periods of fasting or prolonged exercise. They are transported through the bloodstream and readily cross the blood-brain barrier to be used as a source of energy for our brain cells.
Additionally, ketones have gained significant attention in recent years due to their potential therapeutic effects. Research suggests that ketosis, a state in which ketone levels are elevated, may have benefits for conditions such as epilepsy, Alzheimer’s disease, and even certain types of cancer.
Glucose
 On the other hand, glucose is a monosaccharide and the primary source of energy for our bodies. It is commonly referred to as blood sugar and is obtained from the breakdown of carbohydrates in our diet.
On the other hand, glucose is a monosaccharide and the primary source of energy for our bodies. It is commonly referred to as blood sugar and is obtained from the breakdown of carbohydrates in our diet.
Glucose is efficiently metabolized by our cells and serves as a quick and easily accessible source of energy. It is transported through the bloodstream and taken up by various tissues, where it undergoes a series of reactions to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the energy currency of our cells.
Unlike ketones, our brain relies heavily on glucose as its primary fuel source. In fact, the brain consumes around 20% of the total glucose utilized by the body, highlighting its importance in maintaining optimal brain function.
The Differences
Now that we have a basic understanding of ketones and glucose, let’s explore their key differences:
Energy Source:
Ketones are primarily utilized as an alternative energy source when glucose levels are limited, such as during fasting or a low-carbohydrate diet. Glucose, on the other hand, serves as the main source of energy for our bodies under normal conditions.
Metabolic Pathways:
Ketones are produced through the breakdown of fatty acids in the liver, a process known as ketogenesis. Glucose, on the other hand, is derived from the breakdown of carbohydrates through a series of enzymatic reactions.
Brain Fuel:
Ketones can cross the blood-brain barrier and provide an efficient source of energy for our brain cells. In contrast, glucose is the preferred fuel for the brain and is essential for optimal cognitive function.
Therapeutic Potential:
Ketones have shown promise in various therapeutic applications, including epilepsy, neurodegenerative diseases, and cancer. Glucose, on the other hand, does not have the same therapeutic potential but is vital for overall body function.
As we have seen, ketones and glucose play distinct roles in our bodies. While ketones serve as an alternative energy source and have therapeutic potential, glucose is essential for maintaining optimal bodily functions, especially brain function.
It’s important to note that the content provided here is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. If you have any concerns or questions regarding your health, it’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional.
Thank you for joining us on this journey to understand the differences between ketones and glucose. Stay curious, stay informed, and keep exploring the fascinating world of science!
If you are looking for Ketones and Nutritional Ketosis: Basic Terms and Concepts you’ve visit to the right web. We have 5 Pics about Ketones and Nutritional Ketosis: Basic Terms and Concepts like Understanding the Ketogenic Diet: What is Acetone?, Solved: Ketones And Aldehydes Are Hydrated Under Acidic Or… | Chegg.com and also Understanding the Ketogenic Diet: What is Acetone?. Here you go:
Ketones And Nutritional Ketosis: Basic Terms And Concepts
 www.virtahealth.comketosis ketone ketones ketogenic virta
www.virtahealth.comketosis ketone ketones ketogenic virta
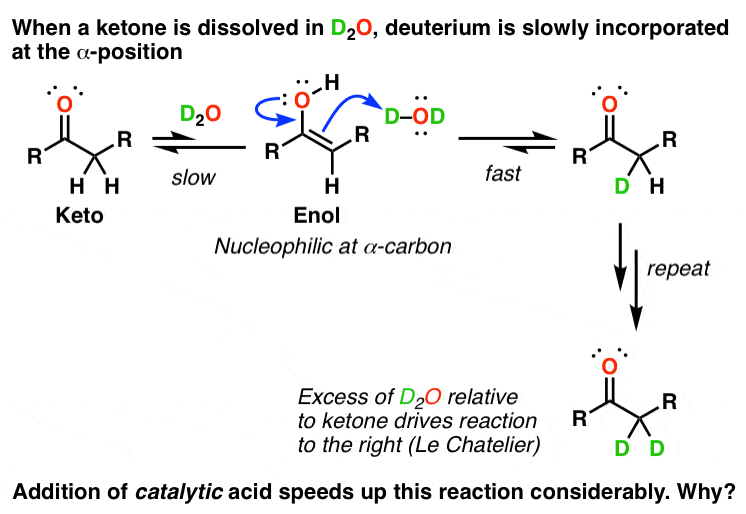
How To Make Keto-enol Tautomerism Waaaaaaay Faster — Master Organic
 masterorganicchemistry.wordpress.comenol keto tautomerism deuterium d2o ketone acids ketones catalyze incorporation chemistry catalysis suddenly
masterorganicchemistry.wordpress.comenol keto tautomerism deuterium d2o ketone acids ketones catalyze incorporation chemistry catalysis suddenly
Difference Between Ketone And Glucose | Difference Between
 www.differencebetween.netketone ketones glucose molecule endurance
www.differencebetween.netketone ketones glucose molecule endurance
Solved: Ketones And Aldehydes Are Hydrated Under Acidic Or… | Chegg.com
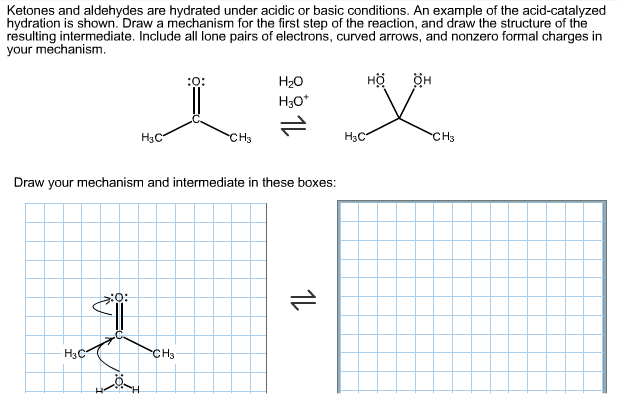 www.chegg.comketones aldehydes acidic hydrated basic under conditions acid example hydration catalyzed solved answer transcribed text show
www.chegg.comketones aldehydes acidic hydrated basic under conditions acid example hydration catalyzed solved answer transcribed text show
Understanding The Ketogenic Diet: What Is Acetone?
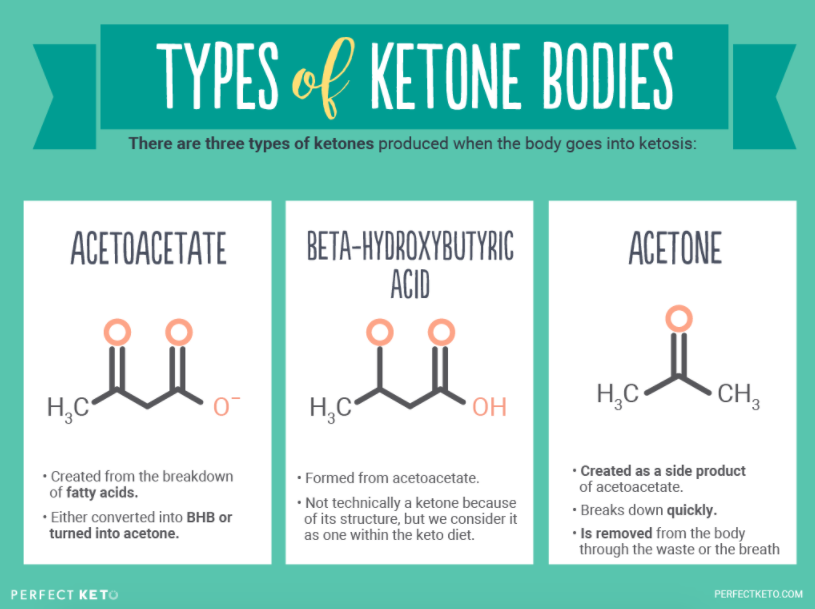 www.perfectketo.comketone ketones acetone bodies acetoacetate body bhb types why diet ketogenic keto fat levels hydroxybutyrate beta ketosis acid look made
www.perfectketo.comketone ketones acetone bodies acetoacetate body bhb types why diet ketogenic keto fat levels hydroxybutyrate beta ketosis acid look made
Ketone ketones glucose molecule endurance. Difference between ketone and glucose. Ketone ketones acetone bodies acetoacetate body bhb types why diet ketogenic keto fat levels hydroxybutyrate beta ketosis acid look made